Short-Run vs. Long-Run Costs
Business must make decisions on whether to spend money now (fixed) or spend money later (variable)
If a firm plans on producing a high amount of output, it might make sense to have a high fixed cost
Conversely, if a firm plans on producing a small amount of output, it might make sense to have a low fixed cost
Choosing the optimal level of fixed cost requires a lot of planning
Long-Run Average Total Cost (LRATC)
Meaning
the relationship between output and average total cost when fixed cost has been chosen to minimize average total cost for each level of output
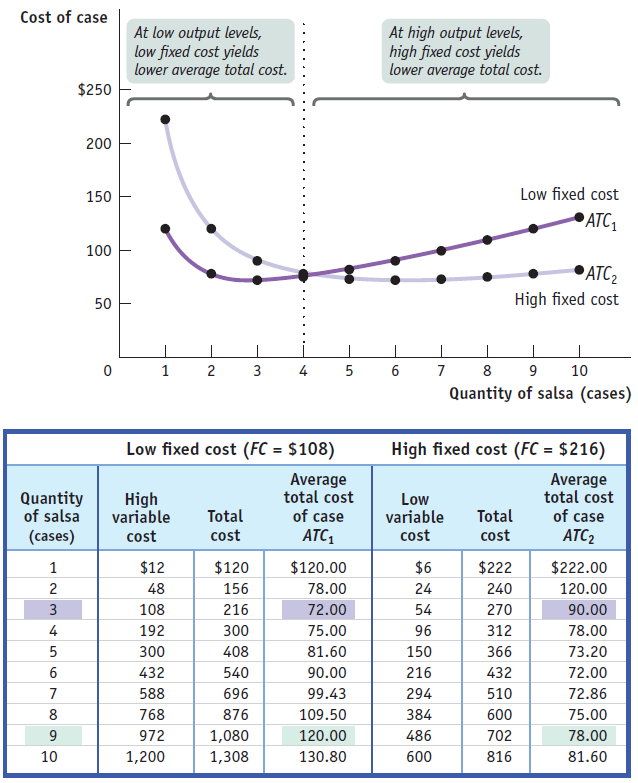
If there are many possible choices of fixed cost, the long-run average total cost curve will have the familiar, smooth U shape.
Graph
![Cost of case Economies of scale Diseconomies ofscale سس سكسر ATC6
ATCg \]RATC 3 Quantity of salsa (cases)](media/image110.png)
Short-run and long-run average total cost curves differ because a firm can choose its fixed cost in the long run.
If Selena has chosen the level of fixed cost that minimizes short-run average total cost at an output of 6 cases, and actually produces 6 cases, then she will be at point C on LRATC and ATC6.
But if she produces only 3 cases, then she will move to point B.
If she expects to produce only 3 cases for a long time, in the long run she will reduce her fixed cost and move to point A on ATC3.
Likewise, if she produces 9 cases (putting her at point Y) and expects to continue this for a long time, she will increase her fixed cost in the long run and move to point X
Example
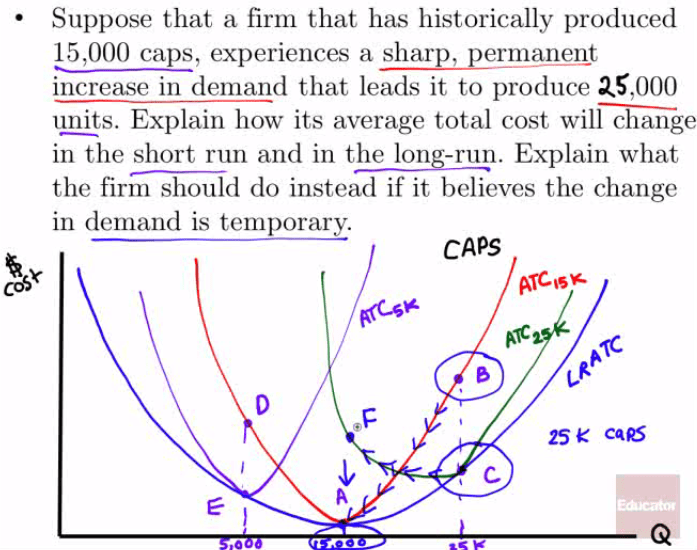
Returns to Scale
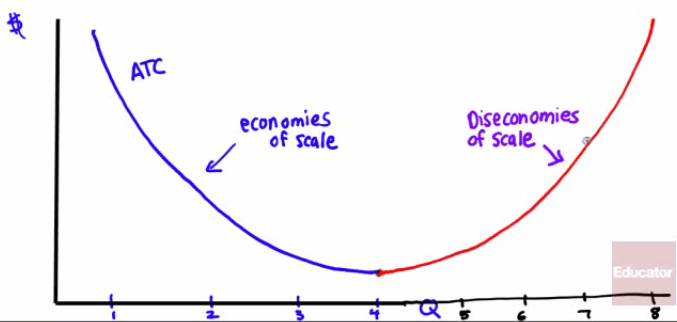
Economies of scale
when long-run average total cost declines as input increases
ATC decreases as Q increases
Diseconomies of scale
when long-run average total cost increases as output increases
ATC increases as Q increases
Graph
Sources of Economies of Scale
Increased specialization that larger output levels allow
- a larger scale of operation means that workers are very specialized individuals
Large initial set-up cost
- in auto manufacturing, electricity generating or petroleum refining, there exist high fixed costs to enter the industry
Network externalities
the effect that one user of a good or service has on the value of that product to other people
When network effect it present, the value of a product or service if dependent on the number of others using it (ie. Telephone, Facebook, Twitter, eBay)
Sunk Cost
Definition
cost that should be ignored when making a decision
A cost that has already happened that cannot be recovered
As the old saying goes, "There's no use crying over spilled milk"
Example
You go to an All You Can Eat Brazilian BBQ Restaurant, pay $40 after eating a salad and you are full.
What's the rational thing to do in order to get your money's worth?
WALK OUT! SUNK COST!
Marginal Benefit > Marginal Cost: Keep doing
Marginal Cost > Marginal Benefit: Leave!
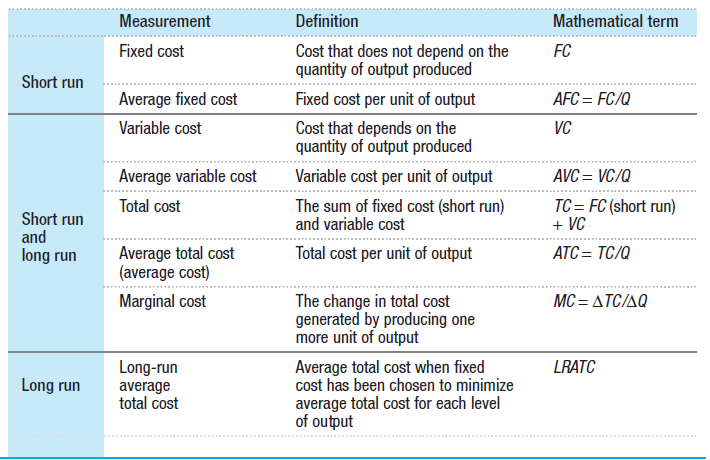
Summary of Costs