Question 5
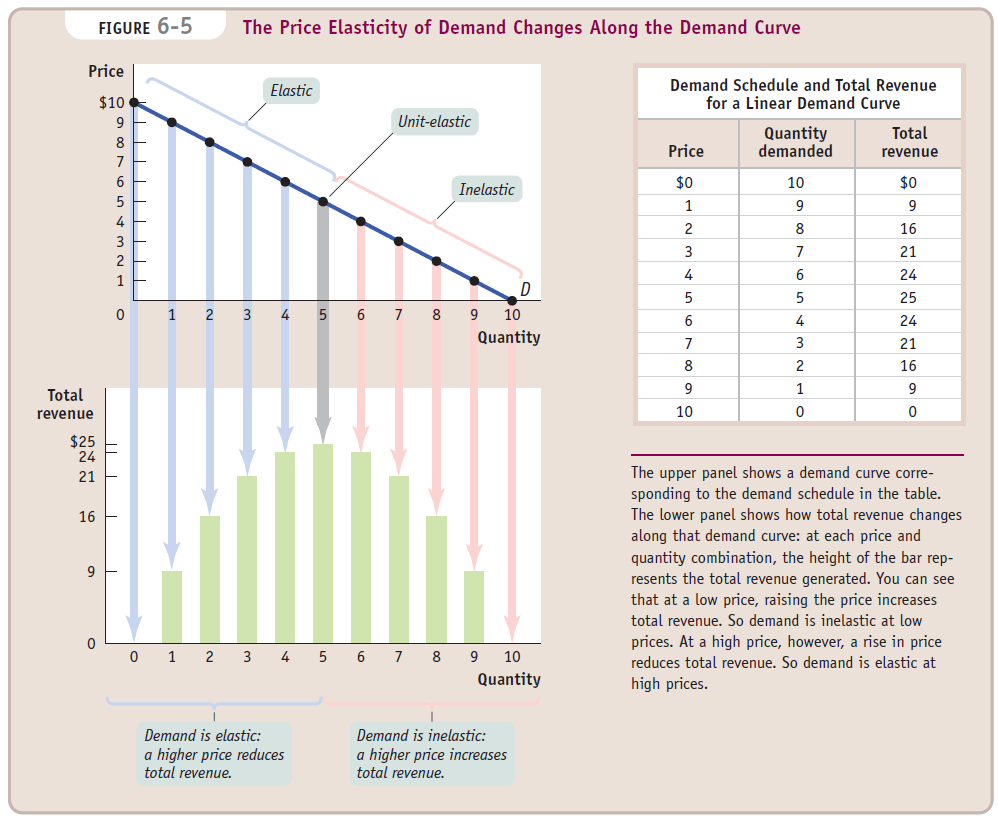
- The total revenue (total cost) remains the same when demand is unit-elastic
Question 8
Average variable costs are increasing when marginal costs are higher than average variable costs
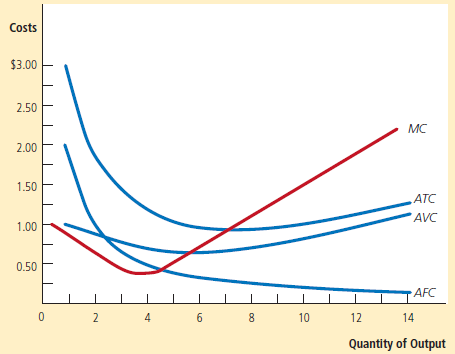
Question 10
If price falls less than AVC, then you should shut down the company.
Long-run (Profitability)

Short-run (Production)

Question 14
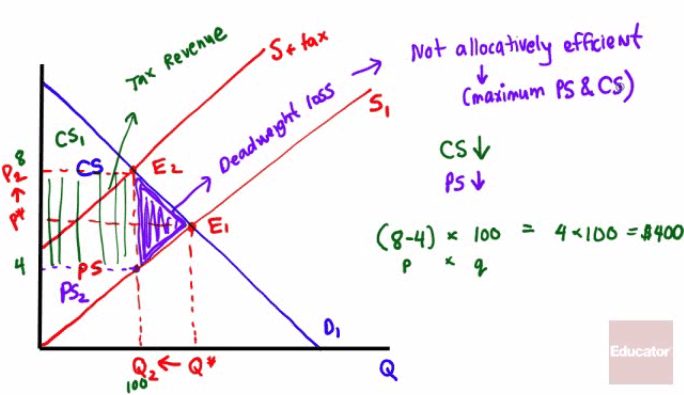
Question 15
- Both consumers and producers bear a part of the total tax burden.
Question 17
Economic Profit = Accounting Profit - Opportunity Cost
In a perfectly competitive industry, the Economic Profit = 0.
So, Account Profit = Opportunity Cost